Variant Filtration
Contents
This view allows you to filter variants to a number of criteria. Further, you can trigger an export of the variants with your current criteria to a downloadable VCF, Excel, or TSV file.
You can open the variant filtration view for each case by first navigating to the case’s detail page and then clicking then Filter Case button on the top right.
On the top of the page, you can see the Variant Filtration Form for setting the parameters for creating your filtration. Below, the results will be displayed after submitting the form.
Note
VarFish will store every query that you make. When loading the filtration form, your previous form settings will be restored and a notification will be displayed to notify you of this.
Note
The implementation of the variant filter in VarFish is monolithic as we use the data from the user submitted form to compile a single, rather large, SQL query from it. This enables us to have a very efficient (in terms of computing time and resources) filtering step. The downside of this is that we can’t track how many variants are actually filtered out by which filter setting.
Variant Filtration Form
Note
As in many places, VarFish offer in-place online help: Move your mouse cursor over any item to display its tooltip description (if it has any).
The form has the following components. Note that some form tabs will be hidden below the More… tab depending on your screen size.
Genotype tab
Frequency tab
Variants & Effects tab
Quality tab
Gene Lists tab
Flags & Comments tab
ClinVar & HGMD tab
Configure Downloads tab
Miscalleneous tab
Filter Import Export tab
Load Presets button
RefSeq / ENSEMBL switch
- Filter & Display button
The little triangle on the right gives access to the Download as File and Submit to MutationDistiller menu entries.
Genotype
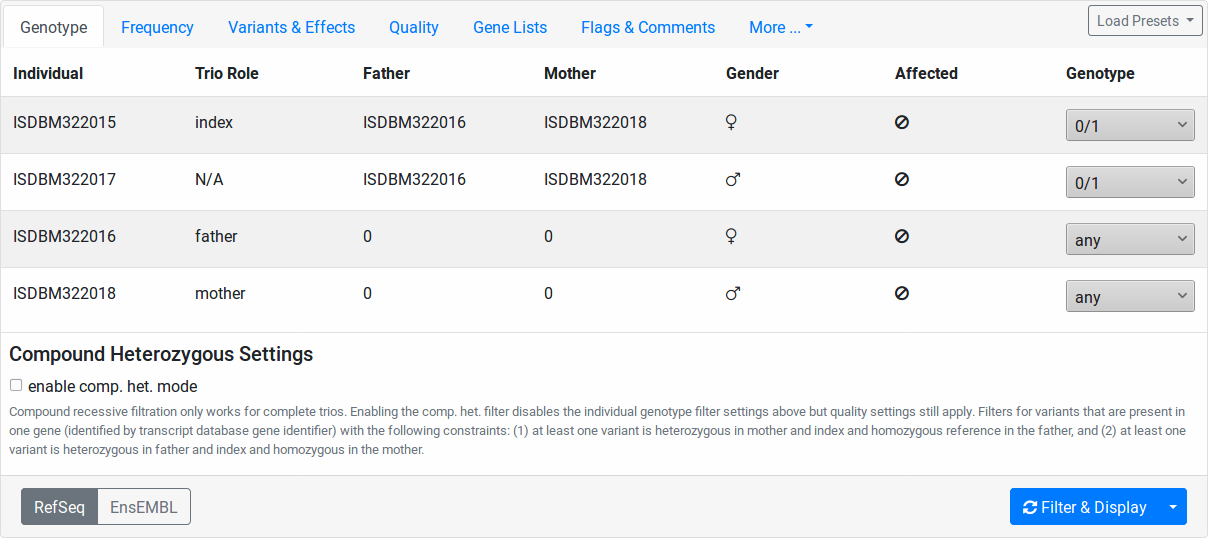
In this tab, the individuals of your pedigree are displayed with their name, father and mother, sex, and disease state.
Here, you can configure the genotype pattern that you want to query for. The Genotype column contains select fields for each of your pedigree individuals. The value meanings are:
- any (default)
Any genotype is allowed.
- 0/0
The genotype of this individual should be reference.
- 0/1
The genotype of this individual should be heterozygous.
- 1/1
The genotype of this individual should be homozygous alternative.
- variant
The genotype of this individual should be heterozygous OR homozygous alternative.
- non-variant
The genotype of this individual should be reference or no-call (
./.).- non-reference
The genotype of this individual should be heterozygous OR homozygous alternative OR no-call (
./.).
Further, you can check the enable comp. het. mode checkbox. In this case, the values of the Genotype column’s select fields are ignored. Instead, the list of variants will be filtered as follows:
All variants are filtered according to the remaining tabs of the filtration form (all except Genotype).
- Two sets of variants are created:
A paternal set with variants that are in heterozygous state in both the index and the father and which are reference in the mother.
A maternal set with variants that are in heterozygous state in both the index and the mother and which are reference in the father.
For each gene occuring in either set, the number of variants are counted, leading to paternal count and maternal count for each gene.
Only those genes where both the paternal and maternal count is above zero are kept.
All variants where the paternal and the maternal count are above zero are reported. This can include variants where the paternal or maternal count is above one.
Note
The compound heterozygous mode currently only works if you have a full trio in your data set (father/mother/child). Further, only the genotypes of these three individuals will be considered in the filtration.
Frequency
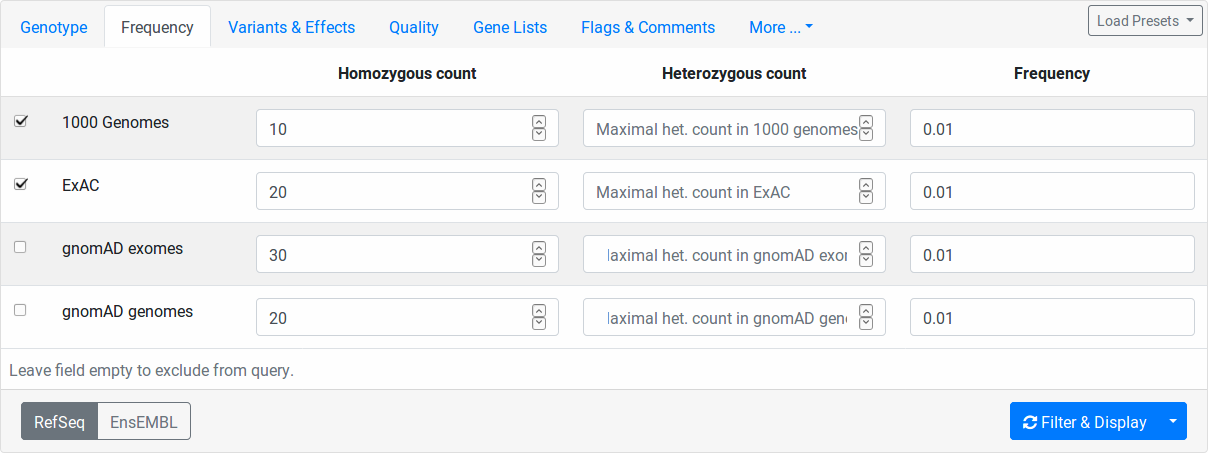
Here you can filter variants by their relative frequency in variation databases or how often they occur within in heterozygous or homozygous state. The population databases are 1000 Genomes Phase 3, ExAC, genomAD exomes, and gnomAD gnomes. You switch on/off a population for consideration by the little checkbox on the left.
The column Homozygous count limits the number of maximal occurences of a variant in homozygous state for each database.
For example, setting 10 for 1000 Genomes, all variants occuring 11 times or more often in the 1000 Genomes dataset will be excluded.
The Heterozygous count field works the same way but for number of heterozygous state.
The Frequency field works as follows.
Here, you specify the maximal frequency in any sub population of the given database.
For example, setting 0.01 for ExAC, you will exclude all variants occuring with a higher frequency than 1% in any sub population, e.g., if the variant has 2% in the African ExAC samples and 0.1% in the European samples, then it will be excluded.
In all homozygous/heterozygous/frequency fields, you can disable the corresponding filter by leaving the field empty.
Variants & Effects
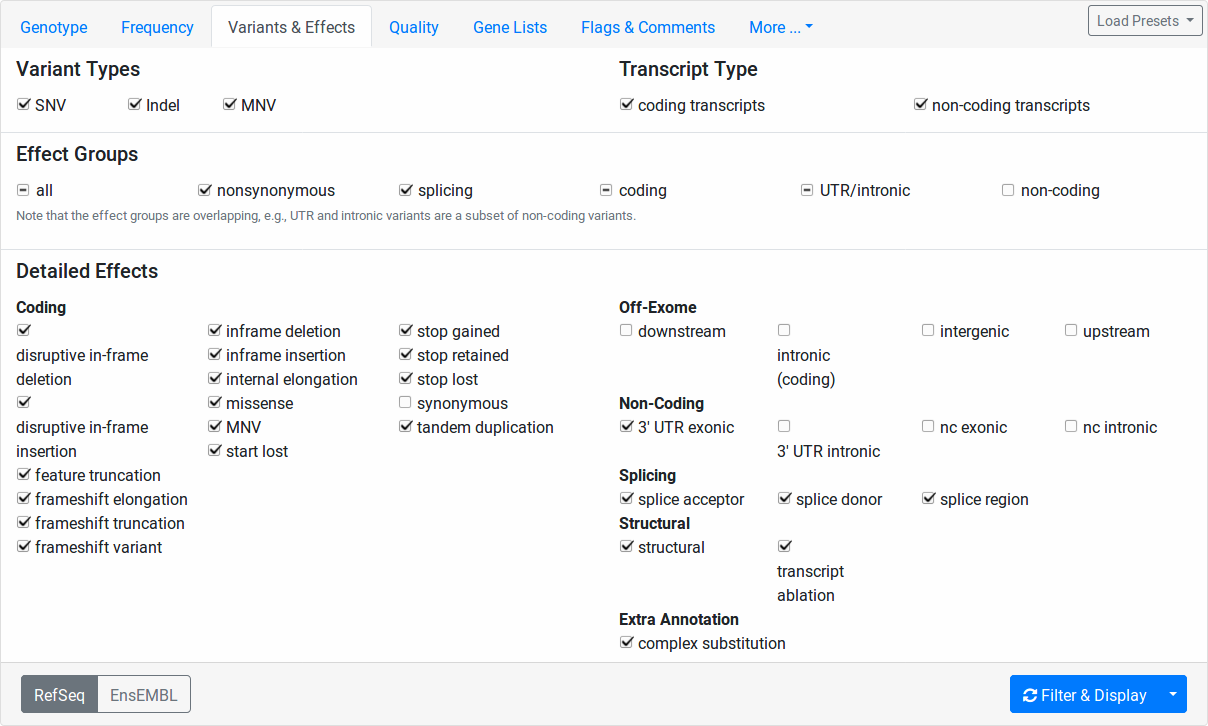
This tab allows for the fine-granular selection of variants based on the variant effects.
The Variant Types section allows you to select whether to include SNVs (single nucleotide variants, e.g., A>C), Indels (insertions or deletions, e.g., AC>T, A>CT, ACT>GG), or MNVs (multi-nucleotide variants where reference and alternative allele have the same number of bases and more than one base is affected, e.g., CC>TT, CCC>TTT).
The Transcript Type section allows you to select whether to include coding and/or non-coding variants.
In the Detailed Effects section, you can perform selection of variants on the finest level of granularity. The Effect Groups allow you to quickly select and unselect fields from the Detailed Effects section.
Quality
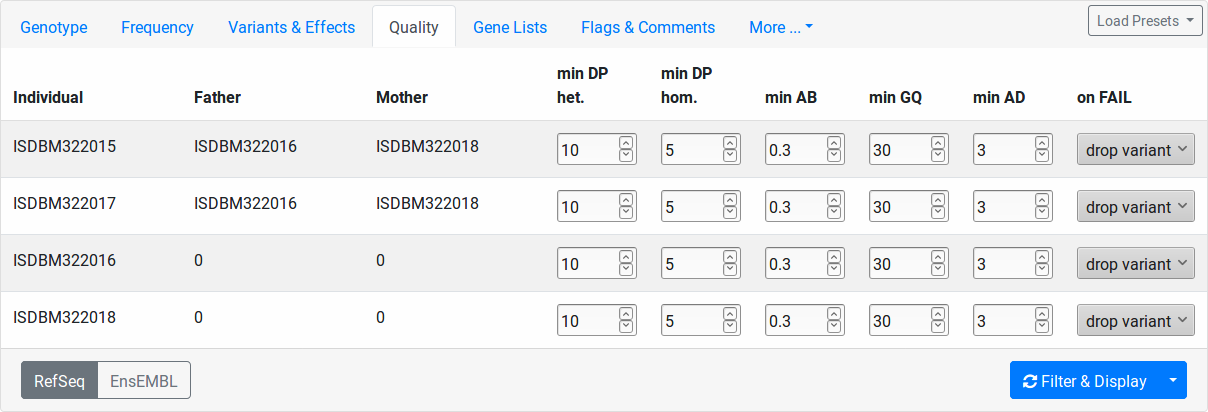
This tab allows you to set quality thresholds on the genotype calls on a per-sample level. Further, you control how calls not passing the threshold in individuals are treated.
- min DP het.
Minimal coverage of heterozygous variants to pass the quality filter.
- min DP hom.
Minimal coverage of homozygous variants to pass the quality filter.
- min AB
Minimal allelic balance. This settings is applied to heterozygous variant calls only. Given a variant with total coverage c and a reads supporting the alter native allele, the allelic balance AB is defined as a/c. A well-balanced variant has an allelic balance that is not too far from 0.5. To pass the quality filer, the allelic balance must be: min AB <= AB <= 1 - min AB.
- min GQ
Minimal (Phred-scaled) genotype quality for variants to pass the quality filter.
- min AD
Minimal number of reads supporting the alternative allele to pass the quality filter.
The “on FAIL” column determines the action to take for variants that don’t pass the quality filter:
- drop variant
The whole variant is removed from the result if the quality filter fails in this individual. This makes a low-quality call in the particular sample remove the variant even if the quality is high in other individuals.
- ignore
The quality filter is ignored for the particular sample.
- no-call
The variant in this individual is counted as “no-call” in the Genotype filter settings.
Gene Lists
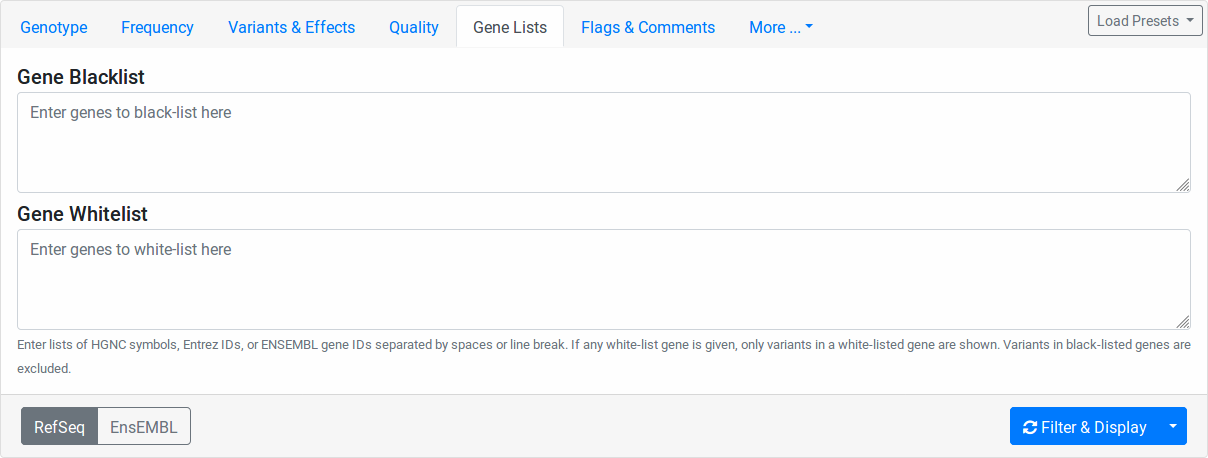
Enter any Entrez gene ID, ENSEMBL gene ID, HGNC/HUGO gene symbol in the Gene Blocklist field to remove variants in this gene from the result list. If a variant affects more than one gene, blocklisting one of them will not blocklist them in the other genes.
Similarly, enter any Entrez gene ID, ENSEMBL gene ID, HGNC/HUGO gene symbol into the Gene Allowlist field to limit variants to those in the allow-listed genes. Leave the allowlist empty to not apply any allow-listing.
Flags & Comments
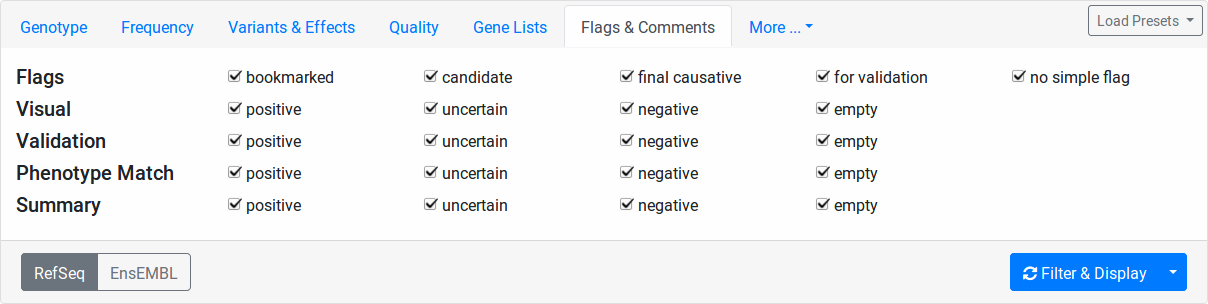
Here you can filter your variants based on the user-provided flags.
ClinVar & HGMD
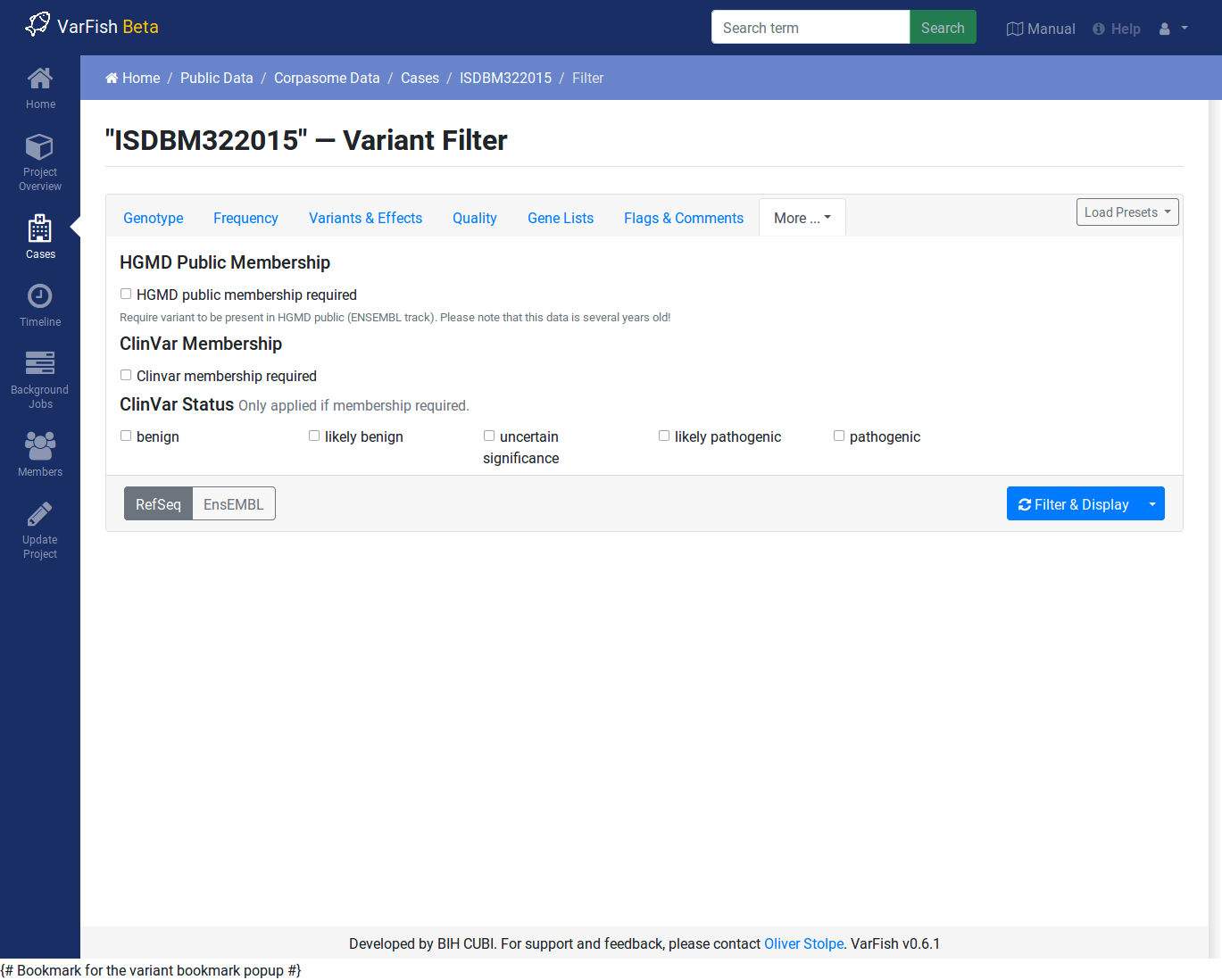
You can use this to require membership in ClinVar and HGMD Public. When requiring ClinVar membership, you can limit the reported variants to those with a particular pathogenicity.
Note that the HGMD Public data is taken from the ENSEMBL browser and is several years behind the current HGMD Public and Professional versions.
Configure Downloads
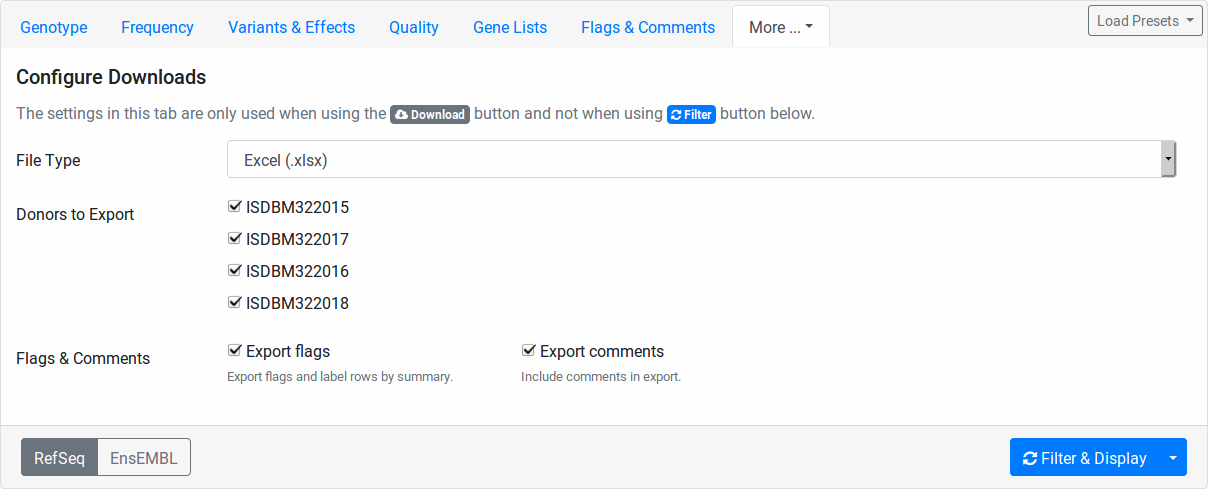
These fields allow you to configure how your file downloads are created. You can select the file type to use for the exprot (Excel, TSV, or VCF).
Further, you can select the individuals to include. This is useful for generating single-individual VCF files if you want to use tool that does not support multi-sample VCF files.
Also, you can select whether you want to export your flags and comments.
Miscalleneous
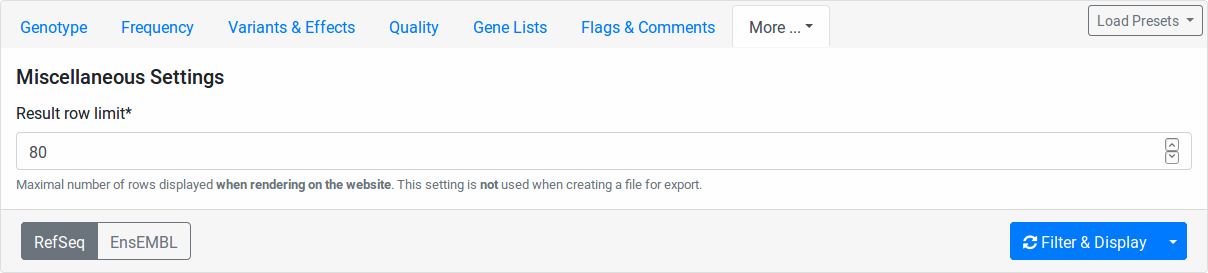
Here you can select a row limit on the online variant display.
This limit will not be applied to your file downloads.
Filter Import Export
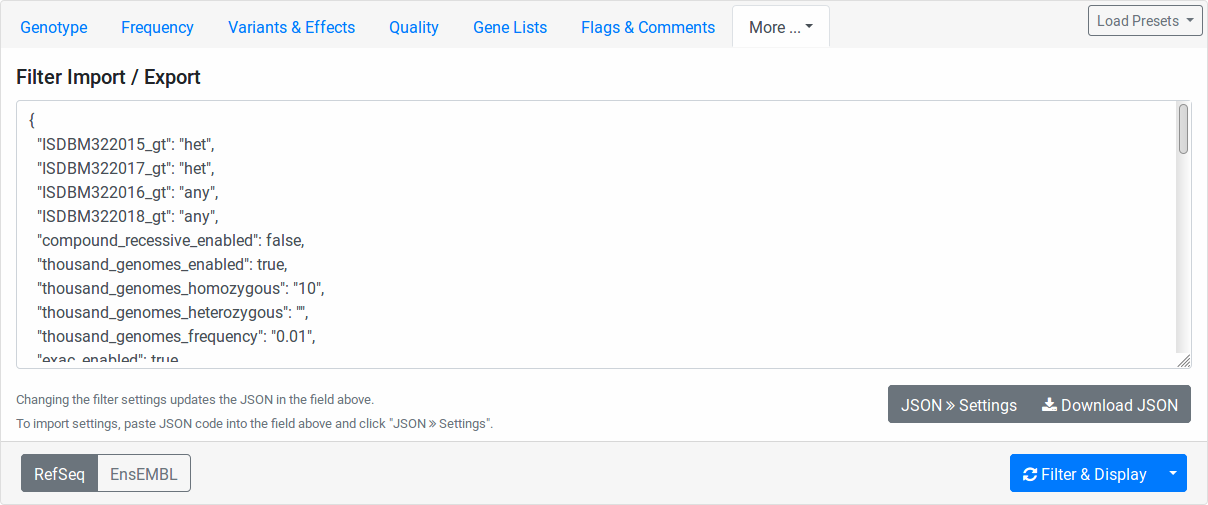
Here you find the configuration stored in JSON format. While the format is machine and not human-oriented, it allows you to save your current form settings in a text file and restore them later.
Click the Download JSON button to download a text file with the value of the text area above. Clicking the JSON >> Settings button applies the changes from the text area to the form. The text area is automatically updated to reflect the current form settings when you change any form field.
Load Presets
Here you find shortcuts to several presets. Note that these are “factory” defaults at the moment. Currently, it is not possible to create your own presets. This will be possible in a future version.
RefSeq / ENSEMBL switch
Use this to choose between RefSeq and ENSEMBL transcripts when filtering for variant effects.
Variant Filtration Results
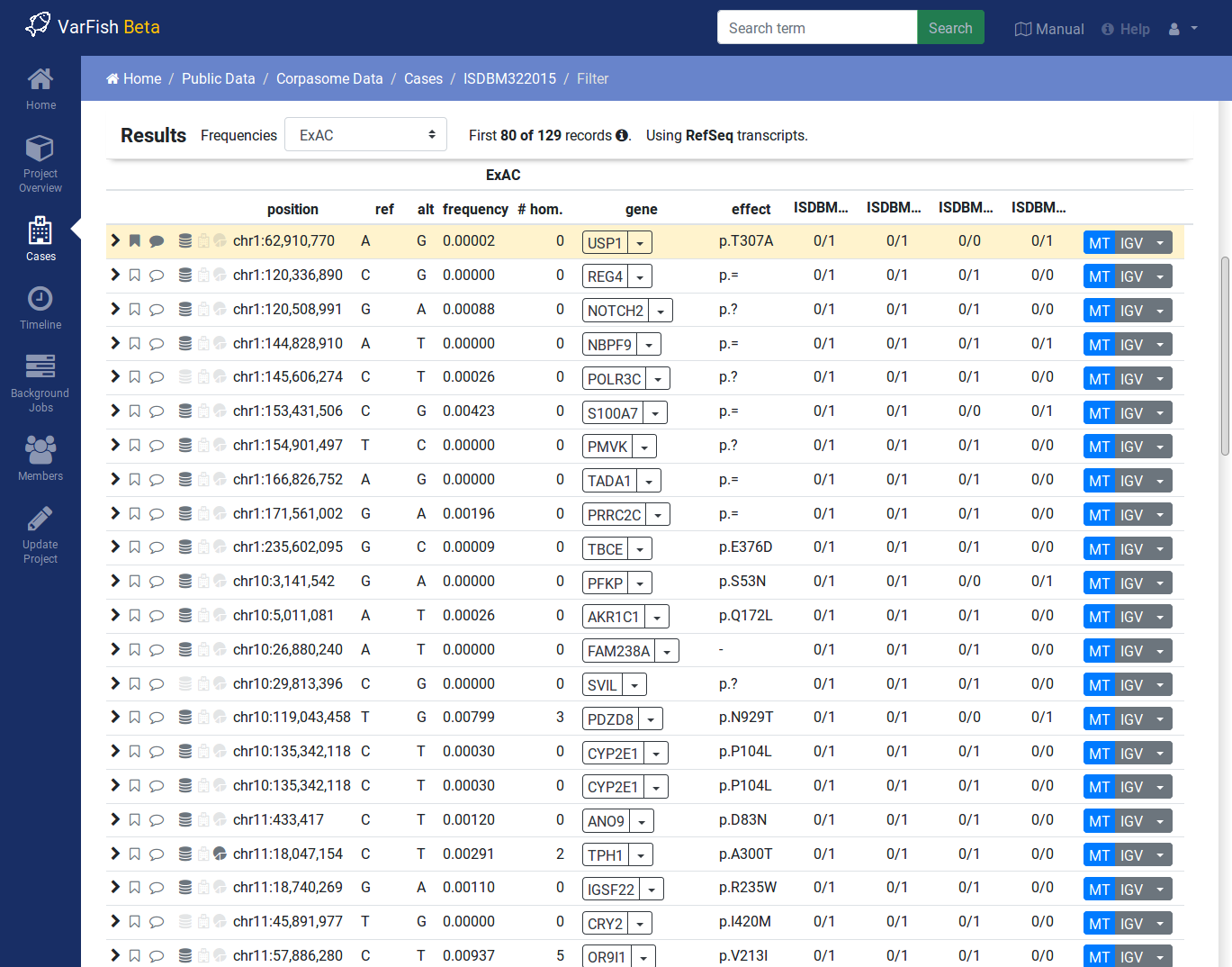
After form submission, the results are displayed below the form.
Filtration Results Header
The header contains a Frequencies switch that allows you to select the database for display population frequencies. Further, it shows the number of displayed and the number of result records. Lastly, it displays the transcript data source used.
Warning
Always monitor the number of displayed vs. total records. You might have to adjust the number of displayed rows so you don’t miss any variants!
Result Rows
The result rows consist of the following elements:
Clicking right-pointing arrow will show you more details on your variant below the result row.
The little bookmark sign indicates whether the variant has been flagged (filled if flags are present). The summary flag status is also indicated by the row color. Click on the bookmark sign to adjust the flags for this variant.
The little speech bubble indicates whether there are any comments for this flag (filled if comments are present).
The little database icon (three disks) indicates dbSNP membership of the variant (dark if present in dbSNP, very light if not). Click on the icon to go to its dbSNP entry.
The little hospital icon indicates ClinVar membership (again dark if present in ClinVar, very light if not).
The little circle indicates membership in HGMD Public (see ClinVar & HGMD for information about HGMD Public age).
The following columns indicate the variant position, reference and alternative bases.
This is followed by the frequency display from the population database selected in the header.
The next column shows the gene symbol, clicking on the little triangle next to it allows you to see the variant in various databases.
The variant effect on the protein level in HGVS notation. Moving the cursor over this field will show a textual explanation of the effect.
The next columns show the genotypes in the individuals. Moving the cursor over this field will show the genotype quality and number of reference and alternative reads.
The MT button will query MutationTaster for this variant.
The IGV button opens the selected locus in IGV if you have it open in the background and activated and the port set to
60151.Clicking the little triangle next to IGV allows you to open the variant locus in various other genome browsers.